
Clonidine is a trusted medication known for its effectiveness in managing hyperkalemia. If you’re searching for a solution to this condition, Clonidine may be the answer you’ve been looking for.
Hyperkalemia can be challenging to deal with, but with Clonidine, you can experience relief and better manage your potassium levels. Don’t let hyperkalemia control your life – try Clonidine today and take control of your health.
Effects of Clonidine
Clonidine is a medication that is commonly used to treat high blood pressure, ADHD, and other conditions. It works by stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain, which leads to the suppression of the sympathetic nervous system. This results in a decrease in heart rate, blood pressure, and the release of certain stress hormones.
Clonidine also has several other effects, including reducing anxiety, improving focus and attention, and promoting relaxation. It can be particularly useful in managing symptoms of anxiety disorders, such as panic attacks and social anxiety.
However, Clonidine can also cause side effects such as drowsiness, dry mouth, constipation, and dizziness. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting Clonidine to discuss potential risks and benefits.
Hyperkalemia Risk
Hyperkalemia is a potential risk associated with the use of Clonidine, a medication commonly prescribed to treat high blood pressure and certain conditions. Hyperkalemia refers to elevated levels of potassium in the blood, which can have serious consequences if not properly managed.
When taking Clonidine, patients should be aware of the possibility of developing hyperkalemia and should monitor their potassium levels regularly. It is important to discuss any concerns or symptoms with a healthcare provider promptly to prevent complications.
Clonidine-induced hyperkalemia can be a serious side effect, but with proper monitoring and management, the risks can be minimized.
Hyperkalemia Risk
Hyperkalemia refers to elevated levels of potassium in the blood, which can be a potential risk associated with the use of Clonidine. This condition can have serious implications on heart function and overall health.
Causes: Clonidine may cause hyperkalemia by affecting the balance of potassium in the body. It can interfere with the normal regulation of potassium levels, leading to an increase in potassium concentration in the blood.
Consequences: Hyperkalemia can result in cardiac arrhythmias, muscle weakness, and potentially life-threatening complications. It is essential to monitor potassium levels regularly when using Clonidine to prevent the occurrence of hyperkalemia.
Prevention: To reduce the risk of hyperkalemia, it is crucial to follow proper dosing guidelines and monitor potassium levels closely during Clonidine therapy. Patients with pre-existing conditions that may predispose them to hyperkalemia should be monitored more frequently.
Causes
Hyperkalemia caused by Clonidine can be attributed to its impact on the sympathetic nervous system.
Clonidine binds to presynaptic alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain, leading to the inhibition of sympathetic outflow. This results in decreased norepinephrine release and decreased activation of beta-adrenergic receptors.
As a consequence, there is a reduction in the release of renin from the kidneys, which ultimately leads to decreased aldosterone secretion from the adrenal glands. Aldosterone plays a crucial role in potassium regulation in the body by promoting potassium excretion in the urine.
Therefore, the use of Clonidine can disrupt the balance of potassium levels in the blood, potentially leading to hyperkalemia.
Mechanism of Action
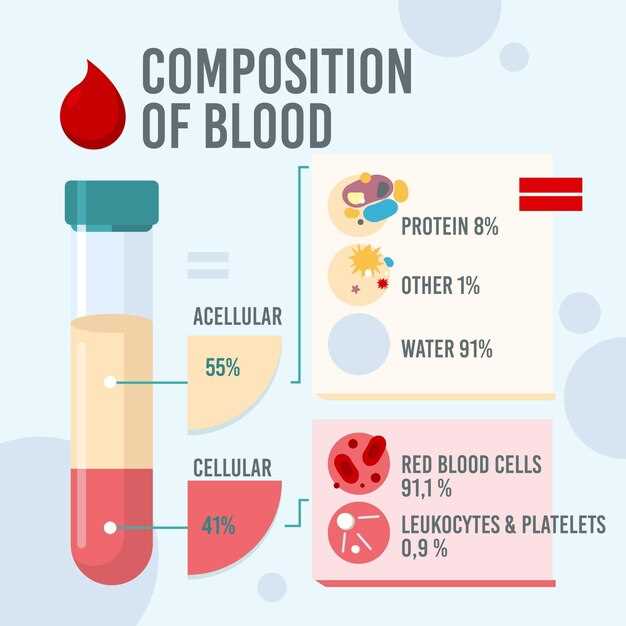
Clonidine works by stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain, which results in a decrease in sympathetic outflow from the central nervous system. By inhibiting the release of norepinephrine, clonidine reduces the activity of the sympathetic nervous system, leading to a decrease in blood pressure, heart rate, and vascular resistance.
This mechanism of action helps manage conditions such as high blood pressure, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and certain pain conditions. Clonidine’s ability to modulate sympathetic activity makes it a valuable treatment option in various medical scenarios, but it also contributes to its potential side effects, including the risk of hyperkalemia.
Symptoms
Hyperkalemia can present with a variety of symptoms ranging from mild to severe. Mild symptoms may include muscle weakness, fatigue, and tingling sensations. As the potassium levels in the blood continue to rise, more severe symptoms such as irregular heartbeat, palpitations, and difficulty breathing may occur.
It is essential to monitor for signs of hyperkalemia, especially in patients taking medications like Clonidine that may increase the risk of developing this condition. Prompt recognition of symptoms can lead to early intervention and treatment, minimizing the potential complications associated with hyperkalemia.
Identifying Hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia is the condition characterized by high levels of potassium in the blood. Identifying hyperkalemia is crucial for proper treatment and management of the condition. Here are some signs and symptoms to watch for:
Symptoms:
1. Weakness or fatigue
2. Nausea and vomiting
3. Irregular heartbeat
4. Muscle weakness or cramping
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment
When hyperkalemia is diagnosed in a patient taking Clonidine, treatment should be initiated promptly to prevent potential complications. The primary goal of treatment is to lower the potassium levels in the blood back to a safe range. Treatment options may vary depending on the severity of the hyperkalemia and the patient’s overall health status.
Some common treatment options for hyperkalemia caused by Clonidine include:
- Discontinuation of Clonidine: In some cases, stopping the use of Clonidine may be necessary to prevent further elevation of potassium levels.
- Administration of Potassium-Lowering Medications: Medications such as Kayexalate may be given to help lower potassium levels in the blood.
- Dietary Changes: A low-potassium diet may be recommended to help regulate potassium levels in the body.
- Monitoring: Regular monitoring of potassium levels through blood tests is essential to track the effectiveness of treatment and ensure that potassium levels stay within a safe range.
It is important for healthcare providers to closely monitor patients with hyperkalemia due to Clonidine and adjust treatment as needed to prevent complications.
